Shedding Light on Skin Cancer: Melanoma Awareness Month
May marks Melanoma Awareness Month, a month dedicated to educating ourselves and others about the dangers of skin cancer, particularly melanoma, and the importance of prevention, early detection, and treatment. While we should be focused on protecting our skin year round, we must be extra diligent as the days grow longer and the sun's intensity increases.
This blog post will discuss the prevalence of skin cancer, its risk factors, and what we can do to protect ourselves from it.
What is Skin Cancer and What Are Its Risk Factors?
Skin cancer is the most common form of cancer in the United States, with melanoma being the most deadly type. Melanoma occurs when the cells that produce pigment in the skin (melanocytes) become cancerous. While it's often associated with excessive sun exposure, melanoma can also develop in areas of the skin not typically exposed to sunlight.
Several factors increase the risk of developing melanoma, including UV exposure, skin type, and family history.
UV Exposure: Prolonged exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun or tanning beds is a significant risk factor for melanoma. UV radiation is particularly associated with melanoma, as it can directly trigger mutations in the melanocyte cells mentioned above and lead to melanoma development.
Skin Tone/Type: Individuals with fair skin, light hair, and light-colored eyes are more susceptible to skin damage from UV radiation. Fair-skinned individuals are more prone to sunburns, a sign of sun damage from excessive UV exposure, and repeated sunburns can increase the risk of skin cancer. Melanoma is more prevalent in people with lighter skin tones.
Family History: A family history of melanoma or other skin cancers increases the risk of developing melanoma. There are also some genetic mutations associated with an increased risk of skin cancer can be passed down within families.
How to Detect Skin Cancer Early and Help Prevent It
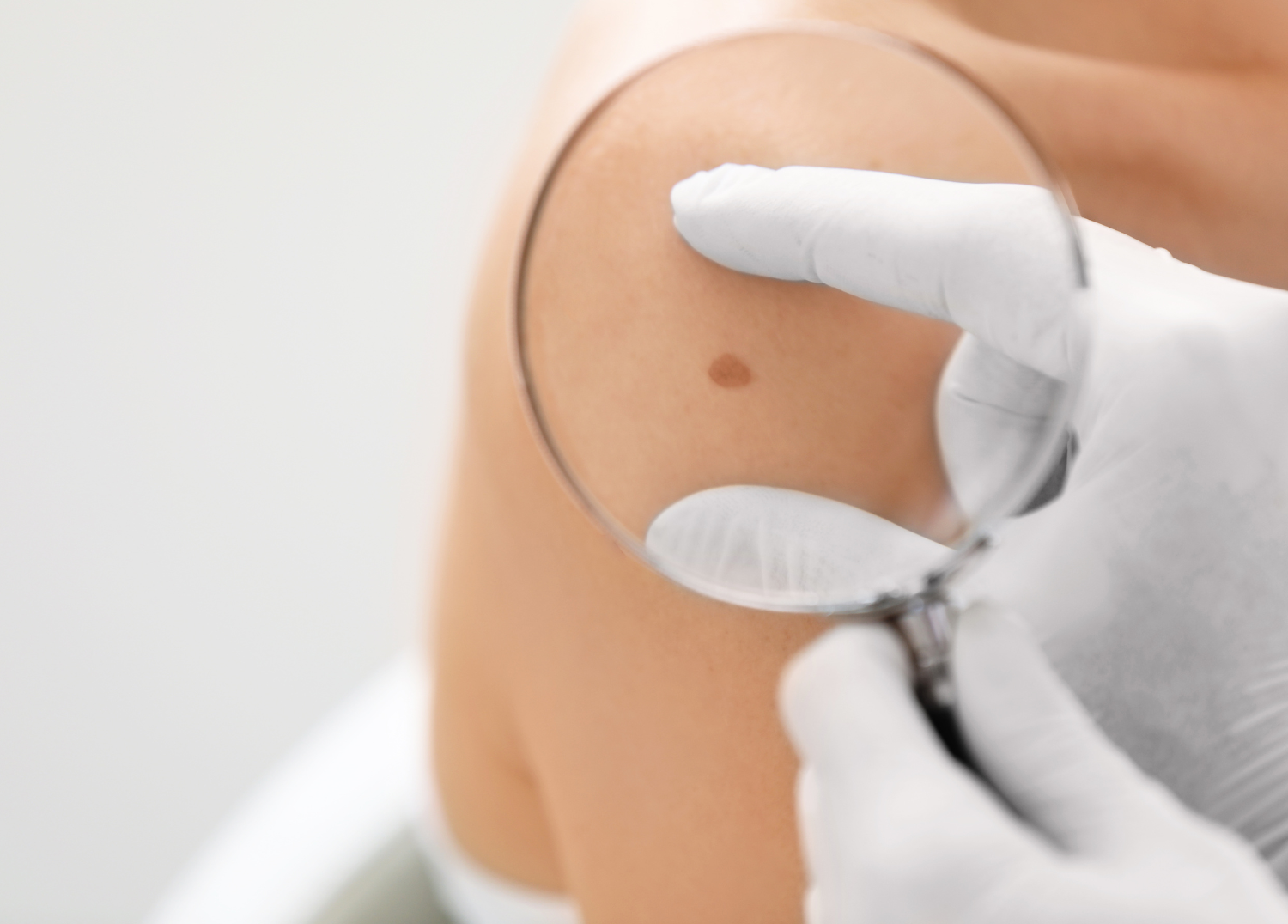
Early detection is crucial for successful treatment of melanoma. Regular skin self-exams and annual visits to a dermatologist can help identify suspicious moles or changes in the skin early on. You should regularly examine the size, shape, color, and texture of moles on your body and note any changes you may see over time.
Prevention is equally important in reducing the risk of melanoma and other skin cancers. You should limit exposure to the sun, especially when the sun's rays are strongest. Wearing protective clothing, wide-brimmed hats, and sunglasses, seeking shade, and using sunscreen with a high SPF when outside can help protect your skin. Avoid using tanning beds, as they can emit high levels of UV radiation that can damage the skin and increase your risk of skin cancer.
As we embrace the summer months and the warmth of the sun, we must also prioritize our skin health. By understanding the risks and signs of skin cancer and adopting good sun-protection habits, we can protecting ourselves from the disease.
This blog is for educational purposes only and based on opinions and publications in public domain.